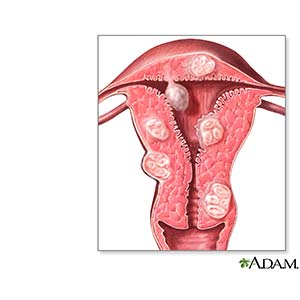
Uterine fibroids are growths found inside your uterus (womb). Uterine fibroids also may be called tumors (lumps) or leiomyomas. Uterine fibroids often appear in groups, or you may have only one. They can be small or large, and they can grow in size. They are almost always benign (not cancer) and likely will not spread to other parts of your body.
 |
Medicines:
- Pain medicine: You may be given medicine to take away or decrease pain. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you take your medicine.
- Hormone medicine: This medicine changes the level of certain hormones and may then help shrink your fibroids.
- Contraceptives: These medicines help prevent pregnancy. They also may help shrink your fibroids.
- Take your medicine as directed: Call your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him if you are taking any vitamins, herbs, or other medicines. Keep a list of the medicines you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
Avoid heavy lifting:
You will need to avoid lifting heavy objects for a period of time after surgery. This helps prevent injury to your surgery wound. Ask your healthcare provider when you may return to your normal daily activities.
Avoid pregnancy:
You will need to avoid pregnancy until you have healed after treatment for your fibroids. Ask your healthcare provider when it is safe to become pregnant.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You feel weak and are more tired than usual.
- You do not feel like your bladder is empty after you urinate. You also may urinate small amounts more often.
- You have new or worse hot flashes.
- You have any questions about your condition or care.
Seek immediate care or call 911 if:
- Your heart begins to race, and you feel faint.
- You have increased vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, or pelvic pressure.
- You have a fever.
- Your leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You cough up blood.
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain. You cough up blood.
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.