Amebiasis is an infection of the intestines. It is caused by the microscopic parasite Entamoeba histolytica.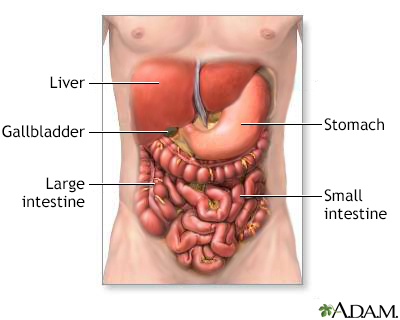
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.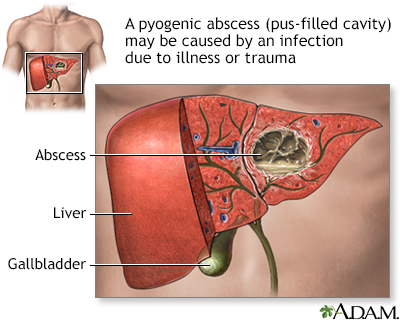
A liver abscess can develop from several different sources, including a blood infection, an abdominal infection, or an abdominal injury which has been become infected. The most common infecting bacteria include E coli, enterococcus, staphylococcus, and streptococcus. Treatment is usually a combination of drainage and prolonged antibiotic therapy.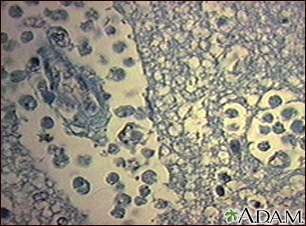
Amebiasis, normally an infection of the intestinal tract, may spread and infect other organs such as the liver or brain. Infection of the brain can be fatal. In this slide, ameba are shown in a sample of brain tissue. Ameba represent a serious infection in immunocompromised individuals. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)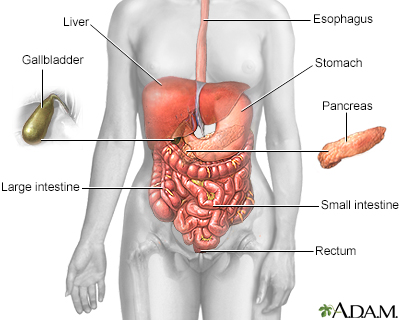
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
A liver abscess can develop from several different sources, including a blood infection, an abdominal infection, or an abdominal injury which has been become infected. The most common infecting bacteria include E coli, enterococcus, staphylococcus, and streptococcus. Treatment is usually a combination of drainage and prolonged antibiotic therapy.
Amebiasis, normally an infection of the intestinal tract, may spread and infect other organs such as the liver or brain. Infection of the brain can be fatal. In this slide, ameba are shown in a sample of brain tissue. Ameba represent a serious infection in immunocompromised individuals. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Causes
E. histolytica can live in the large intestine (colon) without causing damage to the intestine. In some cases, it invades the colon wall, causing colitis, acute dysentery, or long-term (chronic) diarrhea. The infection can also spread through the bloodstream to the liver. In rare cases, it can spread to the lungs, brain, or other organs.
This condition occurs worldwide. It is most common in tropical areas that have crowded living conditions and poor sanitation. Africa, Mexico, parts of South America, and India have major health problems due to this condition.
The parasite may spread:
- Through food or water contaminated with stools
- Through fertilizer made of human waste
- From person to person, particularly by contact with the mouth or rectal area of an infected person
Risk factors for severe amebiasis include:
- Alcohol use
- Cancer
- Malnutrition
- Older or younger age
- Pregnancy
- Recent travel to a tropical region
- Use of corticosteroid medicine to suppress the immune system
In the United States, amebiasis is most common among those who live in institutions or people who have traveled to an area where amebiasis is common.
Symptoms
Most people with this infection do not have symptoms. If symptoms occur, they are seen 7 to 28 days after being exposed to the parasite.
Mild symptoms may include:
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea: passage of 3 to 8 semi-formed stools per day, or passage of soft stools with mucus and occasional blood
- Fatigue
- Excessive gas
- Rectal pain while having a bowel movement (tenesmus)
- Unintentional weight loss
Severe symptoms may include:
- Abdominal tenderness
- Bloody stools, including passage of liquid stools with streaks of blood, passage of 10 to 20 stools per day
- Fever
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. You will be asked about your medical history, especially if you have recently traveled overseas.
Examination of the abdomen may show liver enlargement or tenderness in the abdomen.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood test for amebiasis
- Examination of the inside of the lower large bowel (sigmoidoscopy)
- Stool test
- Microscope examination of stool samples, usually with multiple samples over several days
Treatment
Treatment depends on how severe the infection is. Usually, antibiotics are prescribed.
If you are vomiting, you may be given medicines through a vein (intravenously) until you can take them by mouth. Medicines to stop diarrhea are usually not prescribed, because they can make the condition worse.
After antibiotic treatment, your stool will likely be rechecked to make sure the infection has been cleared.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outcome is usually good with treatment. Usually, the illness lasts about 2 weeks, but it can come back if you do not get treated.
Possible Complications
Complications of amebiasis may include:
- Liver abscess (collection of pus in the liver)
- Medicine side effects, including nausea
- Spread of the parasite through the blood to the liver, lungs, brain, or other organs
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have diarrhea that does not go away or gets worse.
Prevention
When traveling in countries where sanitation is poor, drink purified or boiled water. Do not eat uncooked vegetables or unpeeled fruit. Wash your hands after using the bathroom and before eating.